Understanding the Importance of Circuit Breakers…
Learn what is the importance of circuit breaker for home safety. Understand how circuit breakers work, prevent hazards, and…
Choosing between an AC generator and a DC backup generator? It’s essential to understand the core differences so you can make the right choice for your power needs. Here’s a simplified breakdown to help guide your decision.
There are two major categories of generators:
Before picking one, it’s important to understand how they function and which suits your application best.
All generators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction—converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process happens when mechanical movement in a magnetic field induces electrical current.
Both AC and DC generators utilize electromagnetic induction, but they differ in design and output.
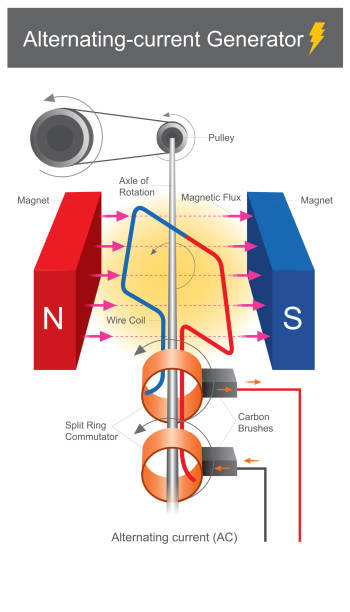
An AC generator produces electricity where the current changes direction periodically. This is due to a fixed coil and a rotating magnet. As the magnet’s poles pass the coil, the current reverses direction, creating alternating current.
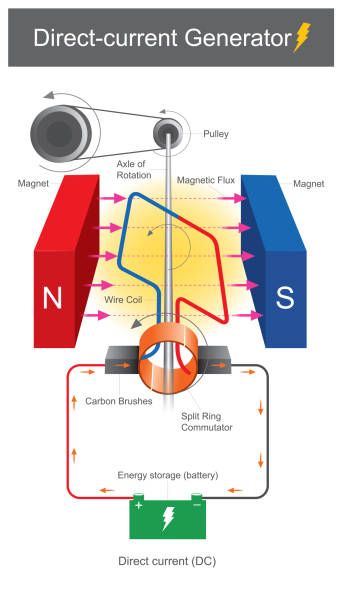
A DC generator, on the other hand, uses a rotating coil within a fixed magnetic field. The current flows in one constant direction thanks to a commutator that ensures unidirectional output.
These structural differences lead to different applications. AC generators are ideal for powering office equipment and household devices, while DC generators are better suited for running large motors and industrial equipment.
Each type has specific strengths:
The frequency of an AC generator is determined by its rotational speed and the number of magnetic poles. Most commonly, the frequency is 60 Hz (60 cycles per second).
In certain situations, you may need to convert power forms:
While AC generators are more commonly used, the right choice depends on your specific requirements. Whether you’re powering small appliances or industrial motors, understanding the differences between AC and DC generators ensures a more informed investment.
Learn what is the importance of circuit breaker for home safety. Understand how circuit breakers work, prevent hazards, and…
Discover the key differences between AC generator vs DC generator. Compare AC vs DC generators to learn their working,…
Want to know how to soundproof your noisy generator? The easiest way is to make a soundproof box. Learn…